Configuration options
Discover configuration options for your BugSnag integration.
Setting configuration options
Many configuration options can be set in your Info.plist file under the bugsnag key. These will be shared with the BugSnag Error Monitoring SDK, if in use.
Configuration options that are for the Performance SDK only – or whose value you require to be different for Performance – are located inside a performance sub-key:
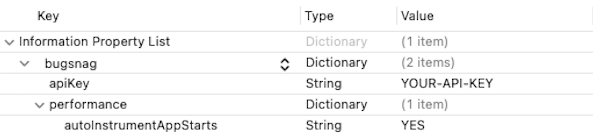
Or in XML:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>apiKey</key>
<string>YOUR-API-KEY</string>
<key>performance</key>
<dict>
<key>autoInstrumentAppStarts</key>
<true/>
</dict>
</dict>
The BugsnagPerformance client can then simply be started using:
[BugsnagPerformance start];
BugsnagPerformance.start()
Alternatively, configuration options can be specified in code by creating a BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration object and passing it to the client:
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.appVersion = @"1.0.0-alpha";
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.appVersion = "1.0.0-alpha"
BugsnagPerformance.start(with: config)
loadConfig uses your Info.plist file to set initial configuration values, allowing you to augment and override the values before they are used to start BugSnag. You can use the BugsnagConfiguration initializer with an API key to avoid using the properties file.
Available options
API key
The API key used for performance data sent to BugSnag.
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.apiKey = "YOUR-API-KEY";
BugsnagPerformance.start(with: config)
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.apiKey = @"YOUR-API-KEY";
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
Or in your Info.plist:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>apiKey</key>
<string>YOUR-API-KEY</string>
</dict>
You can find your API key in your project’s settings (shortcut: gs) in the dashboard.
App version information
Setting your app’s version information in configuration allows you to see performance data for a specific release.
BugSnag captures the built-in values of CFBundleVersion and CFBundleShortVersionString as the app’s version and bundle version by default. This can be overridden in configuration if required:
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.appVersion = @"5.3.55";
config.bundleVersion = @"5.3.55.2";
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.appVersion = "5.3.55"
config.bundleVersion = "5.3.55.2"
BugsnagPerformance.start(configuration: config)
Or in your Info.plist:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>appVersion</key>
<string>5.3.55</string>
<key>bundleVersion</key>
<string>5.3.55.2</string>
</dict>
Auto instrumentation
The instrumentation added to your app to capture measurements can be disabled entirely using the following configuration options:
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.autoInstrumentAppStarts = NO;
config.autoInstrumentViewControllers = NO;
config.autoInstrumentNetworkRequests = NO;
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.autoInstrumentAppStarts = false
config.autoInstrumentViewControllers = false
config.autoInstrumentNetworkRequests = false
BugsnagPerformance.start(configuration: config)
Or in your Info.plist:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>performance</key>
<dict>
<key>autoInstrumentAppStarts</key>
<false/>
<key>autoInstrumentViewControllers</key>
<false/>
<key>autoInstrumentNetworkRequests</key>
<false/>
</dict>
</dict>
You can instead send these measurements by calling startViewLoadSpan and reportNetworkRequestSpan methods in the appropriate places in your app.
Custom attribute limits
The following configuration options can be used to increase the size of custom attribute data that can be stored in each span:
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.attributeCountLimit = 200;
config.attributeStringValueLimit = 5000;
config.attributeArrayLengthLimit = 5000;
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.attributeCountLimit = 200
config.attributeStringValueLimit = 5000
config.attributeArrayLengthLimit = 5000
BugsnagPerformance.start(configuration: config)
Or in your Info.plist:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>performance</key>
<dict>
<key>attributeCountLimit</key>
<integer>200</integer>
<key>attributeStringValueLimit</key>
<integer>5000</integer>
<key>attributeArrayLengthLimit</key>
<integer>5000</integer>
</dict>
</dict>
The number of attributes is limited to 128 by default and subsequent attributes are dropped. The limit can be increased up to 1000.
Individual string values are limited to 1024 by default and array values to 1000 with excess characters and elements being truncated. These limits can both be increased up to 10,000.
The key used for the attribute has a fixed limit of 128. Attributes with a longer key will be dropped.
Care should be taken to avoid adding excessive data as oversized span payloads are rejected by the BugSnag API. If the payload limits are being reached for your project, a warning will be displayed on your Performance dashboard.
Enabled system metrics
Use the enabled metrics configuration option to start capturing system metrics in your custom spans:
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.enabledMetrics.rendering = YES;
config.enabledMetrics.cpu = YES;
config.enabledMetrics.memory = YES;
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.enabledMetrics.rendering = true
config.enabledMetrics.cpu = true
config.enabledMetrics.memory = true
BugsnagPerformance.start(configuration: config)
For more information about this feature, please see our System metrics guide.
Endpoint
By default we will send trace and span data to the address of our hosted traces endpoint.
If you are using BugSnag On-premise you’ll need to set this to your Trace Server endpoint.
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.endpoint = @"https://otlp.example.com/v1/traces";
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.endpoint = "https://otlp.example.com/v1/traces"
BugsnagPerformance.start(configuration: config)
Or in your Info.plist:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>apiKey</key>
<string>YOUR-API-KEY</string>
<key>performance</key>
<dict>
<key>endpoint</key>
<string>https://otlp.example.com/v1/traces</string>
</dict>
</dict>
Network request callback
You can control which network requests are captured and sanitize the URL string sent to your BugSnag dashboard using the networkRequestCallback configuration option. The network request span will be transmitted to BugSnag using the url in the returned object, or will not be sent at all if the url is set to nil:
config.networkRequestCallback = ^BugsnagPerformanceNetworkRequestInfo * _Nonnull(BugsnagPerformanceNetworkRequestInfo * _Nonnull info) {
NSURL *url = info.url;
if ([url.host isEqual: @"no-track.com"]) {
info.url = nil;
return info;
}
NSError *error = nil;
NSRegularExpression *regex = [NSRegularExpression regularExpressionWithPattern:@"account/[0-9]+" options:NSRegularExpressionCaseInsensitive error:&error];
if (error != nil) {
return info;
}
NSString *urlString = info.url.absoluteString;
NSString *newUrlString = [regex stringByReplacingMatchesInString:urlString
options:0
range:NSMakeRange(0, urlString.length) withTemplate:@"account/[account-id]"];
info.url = [NSURL URLWithString:newUrlString];
return info;
};
config.networkRequestCallback = { (info: BugsnagPerformanceNetworkRequestInfo) -> BugsnagPerformanceNetworkRequestInfo in
let url = info.url!
if (url.host() == "no-track.com") {
info.url = nil
return info
}
let urlString = url.absoluteString
info.url = URL(string: urlString.replacing(/account\/[0-9]+/, with: "account/[account-id]"))
return info
}
Release stages
Setting a release stage in your configuration allows you to filter performance data by different stages of the application release process (development, production, etc) in the BugSnag dashboard. The release stage is automatically set to “production”, unless the app is built with debug enabled in which case it will be set to “development”.
If you wish to override this, you can do so by setting the releaseStage configuration option:
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.releaseStage = @"testing";
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.releaseStage = "testing"
BugsnagPerformance.start(configuration: config)
Or in your Info.plist:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>releaseStage</key>
<string>testing</string>
</dict>
You can also limit which builds send performance data by setting the enabledReleaseStages configuration option:
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.enabledReleaseStages = [NSSet setWithArray:@[@"production", @"development", @"testing"]];
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.enabledReleaseStages = ["production", "development", "testing"]
BugsnagPerformance.start(configuration: config)
Or in your Info.plist:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>enabledReleaseStages</key>
<array>
<string>production</string>
<string>development</string>
<string>testing</string>
</array>
</dict>
By default, performance data will be sent for all stages.
Sampling probability
By default, the SDK uses BugSnag’s sampling mechanism to spread the span quota in your plan over a month with a constantly adjusted probability that a given user interaction will be recorded. If you are controlling the sampling yourself – such as using an OpenTelemetry Collector – the sampling probability can be fixed to a value between 0 and 1 to send a fixed proportion.
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.setSamplingProbability(1.0);
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.samplingProbability = 1.0
BugsnagPerformance.start(configuration: config)
When a sampling probability is set explicitly, the captured spans will be counted towards your unmanaged quota. See the Sampling of performance data guide for details.
Service name
A readable identifier for your app to populate the service.name attribute in captured spans.
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.setServiceName(@"ZippyApp");
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.serviceName = "ZippyApp"
BugsnagPerformance.start(configuration: config)
Or in your Info.plist:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>performance</key>
<dict>
<key>serviceName</key>
<string>ZippyApp</string>
</dict>
</dict>
If you are using a collector, you must configure a service name mapping to match spans from your application to the correct project in BugSnag. By default, the service name is the main bundleIdentifier of the app.
Span callbacks
Callback functions can be registered to transform and filter spans before they are sent to BugSnag:
BugsnagPerformanceSpan *span = [BugsnagPerformance startSpanWithName:@"login"];
[span setAttribute:@"device.locale" withValue:@"en-US"];
let span = BugsnagPerformance.startSpan(name: "login")
span.setAttribute("device.locale", withValue: "en-US")
These callbacks can be executed with a high frequency, so care should be taken not to perform complex operations that will have a detrimental effect on performance. To aid diagnostics, the amount of time taken for the callbacks to run is captured in the bugsnag.span.callbacks_duration attribute and shown on the span details panel on the Performance dashboard.
You can perform any operation on the span during the callback, but you should avoid ending the span from inside the callback to prevent a recursive loop.
The return value from the callback determines whether the span will be sent. When a span is discarded, it doesn’t affect other spans in the trace. Therefore returning false in your callback will result in an incomplete trace being shown in your dashboard. In general we recommend returning true in all cases to allow the built-in probability-based sampling to run without potential biases in the aggregated data.
Trace propagation
Enabling this option sends OpenTelemetry compatible trace context headers on network requests made to your servers. We recommend only sending this information to servers that are under your control and instrumented by OpenTelemetry.
This is enabled by setting the tracePropagationUrls configuration option to control which URLs should include the header:
BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration *config = [BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration loadConfig];
config.tracePropagationUrls = [NSSet setWithArray: @[
[NSRegularExpression regularExpressionWithPattern:
@"^(http(s)?(://))?(www\\.)?example\\.com(/.*)?$" options:0 error:nil]
]];
[BugsnagPerformance startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagPerformanceConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.tracePropagationUrls = [
try! NSRegularExpression(pattern: "^(http(s)?(://))?(www\\.)?example\\.com(/.*)?$")
]
BugsnagPerformance.start(configuration: config)
Or in your Info.plist:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>performance</key>
<dict>
<key>tracePropagationUrls</key>
<array>
<string>^(http(s)?(://))?(www\.)?example\.com(/.*)?$</string>
</array>
</dict>
</dict>
Once configured, you will be able to see full distributed traces in your dashboard.