watchOS integration guide
Add BugSnag to your watchOS projects for automatic Apple Watch crash reporting — automatically capture and report crashes in released applications.
New to BugSnag? Create an account
watchOS is a restrictive environment, compared to other Apple OS’s. BugSnag will automatically report unhandled exceptions but OOMs, app hangs, thermal kills, stack overflows, Mach exceptions, POSIX signals, memory access issues, and Swift fatal errors cannot be detected.
Installation
Using CocoaPods
Add the Bugsnag pod to your Podfile:
pod 'Bugsnag'
Don’t forget to run pod install after updating your Podfile.
Using Swift Package Manager
Open your Xcode project and select File → Add Packages…
Search for https://github.com/bugsnag/bugsnag-cocoa as the package URL
Set Dependency Rule exact version to v6.35.0, then click Add Package.
Using Carthage
Add Bugsnag to your Cartfile:
github "bugsnag/bugsnag-cocoa"
Then run Carthage to generate the framework to add to your project:
carthage update --use-xcframeworks --platform watchos
Drag Bugsnag.framework from Carthage/Build to your project.
Manual installation
Clone the BugSnag GitHub repository:
git clone --branch v6.35.0 https://github.com/bugsnag/bugsnag-cocoa
Drag Bugsnag.xcodeproj into your Xcode workspace.
Select your project in the Project Navigator and in the project editor that appears, select your app’s WatchKit extension target.
Under the General tab, click the Frameworks, Libraries and Embedded Content section’s + button and select Bugsnag.framework (from ‘Bugsnag-watchOS’).
The latest available version of bugsnag-cocoa is v6.35.0.
Basic configuration
Configure your API key by adding a bugsnag Dictionary to your WatchKit extension’s Info.plist file:
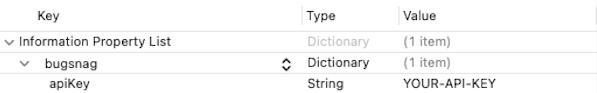
Or in XML:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>apiKey</key>
<string>YOUR-API-KEY</string>
</dict>
You can find your API key in your project’s settings (shortcut: gs) in the dashboard.
Extension Delegate
If your app extension implements an extension delegate, import the Bugsnag module and initialize Bugsnag in the applicationDidFinishLaunching: method:
#import <Bugsnag/Bugsnag.h>
@implementation ExtensionDelegate
- (void)applicationDidFinishLaunching {
[Bugsnag start];
return YES;
}
import Bugsnag
class ExtensionDelegate: NSObject, WKExtensionDelegate {
func applicationDidFinishLaunching() {
Bugsnag.start()
}
}
SwiftUI App Life Cycle
If your app extension adopts the SwiftUI App Life Cycle and does not implement an extension delegate, import the Bugsnag module and initialize Bugsnag within the App conformer’s initializer:
import Bugsnag
@main
struct SwiftUIApp: App {
init() {
Bugsnag.start()
}
}
Network request breadcrumbs
If your app makes network requests via URLSession, you can install the BugsnagNetworkRequestPlugin to capture network requests as breadcrumbs in your error reports. For installation instructions, see our Customizing breadcrumbs guide.
Further configuration
If you’d like to configure Bugsnag further, check out the configuration options reference.
Showing full stacktraces
Stacktraces from Apple platforms include backtraces with memory addresses, but symbolication is required to replace the memory addresses with human-readable function names, file paths, and line numbers. Follow the Showing full stacktraces guide to configure symbolication during your build and release process.
Reporting unhandled exceptions
After completing installation and basic configuration, unhandled exceptions and NSAssert assertion failures (in non-release builds) will be reported and automatically appear on your Bugsnag dashboard.
watchOS is a restrictive environment, compared to other Apple OS’s. BugSnag will automatically report unhandled exceptions but OOMs, app hangs, thermal kills, stack overflows, Mach exceptions, POSIX signals, memory access issues, and Swift fatal errors cannot be detected.
Unhandled exceptions are sent to your Bugsnag dashboard when the app next launches. They will not be reported when the debugger is attached.
Reporting handled exceptions
If you would like to send handled exceptions to Bugsnag, you can pass any NSError object to Bugsnag’s notifyError method:
NSError *error = nil;
BOOL success = [[NSFileManager defaultManager] removeItemAtPath:@"//invalid/file" error:&error];
if (!success) {
[Bugsnag notifyError:error];
}
do {
try FileManager.default.removeItem(atPath:"//invalid/file")
} catch {
Bugsnag.notifyError(error);
}
Instances of NSException can be sent using the notify method:
@try {
[NSJSONSerialization dataWithJSONObject:badlyFormattedJson options:0 error:nil];
} @catch (NSException* exception) {
[Bugsnag notify:exception];
}
let exception = NSException(name:NSExceptionName(rawValue: "NamedException"),
reason:"Something happened",
userInfo:nil)
Bugsnag.notify(exception)
Adding diagnostics or adjusting severity
It can often be helpful to adjust the severity or attach custom diagnostics to handled exceptions. For more information, see Reporting handled errors.
Sending diagnostic data
Automatically captured diagnostics
BugSnag will automatically capture and attach the following diagnostic data to every exception report:
- Stack trace for the error.
- App state including running time and time in foreground.
- Build information including name, version/build and release stage.
- Device specification including model, OS version and total memory.
- System state including free memory and available disk space.
Due to restrictions in watchOS, C++ exceptions do not contain stacktraces.
For more information see Automatically captured data.
Attaching custom diagnostics
It can often be helpful to attach application-specific diagnostic data to error reports. This can be accomplished by setting a callback which will be invoked before any reports are sent to BugSnag:
BugsnagConfiguration *config = [BugsnagConfiguration loadConfig];
[config addOnSendErrorBlock:^BOOL (BugsnagEvent *event) {
[event addMetadata:@"Acme Co." withKey:@"name" toSection:@"account"];
[event addMetadata:@(YES) withKey:@"paying_customer" toSection:@"account"];
// Return `NO` if you'd like to stop this error being reported
return YES;
}];
[Bugsnag startWithConfiguration:config];
let config = BugsnagConfiguration.loadConfig()
config.addOnSendError { (event) -> Bool in
event.addMetadata("Acme Co.", key:"name", section:"account")
event.addMetadata(true, key:"paying_customer", section:"account")
// Return `false` if you'd like to stop this error being reported
return true
}
Bugsnag.start(with: config)
For more information, see Customizing error reports.
Identifying users
In order to correlate errors with customer reports, or to see a list of users who experienced each error, it is helpful to capture and display user information. BugSnag includes helpers for attaching an identifier, email address and name to reports that will be searchable in the dashboard.
By default we will generate a unique ID and send this ID along with every error report from an individual device. If you would like to override this identifier you can set the user ID property.
[Bugsnag setUser:@"3" withEmail:@"bugs.nag@bugsnag.com" andName:@"Bugs Nag"];
Bugsnag.setUser("3", withEmail: "bugs.nag@bugsnag.com", andName: "Bugs Nag")
For more information, see Adding user data.
Logging breadcrumbs
In order to understand what happened in your application before each error, it can be helpful to leave short log statements that we call breadcrumbs. A configurable number of breadcrumbs are attached to each error report to help diagnose what events led to the error.
Automatically captured breadcrumbs
By default, BugSnag captures common events including:
- Thermal state changes
- Non-fatal errors
Network request breadcrumbs
If your app makes network requests via URLSession, you can install the BugsnagNetworkRequestPlugin to capture network requests as breadcrumbs in your error reports. For installation instructions, see our Customizing breadcrumbs guide.
Leaving custom breadcrumbs
You can use the leaveBreadcrumb method to log potentially useful events in your own applications:
[Bugsnag leaveBreadcrumbWithMessage:@"Button tapped"];
Bugsnag.leaveBreadcrumb(withMessage: "Button tapped")
Bugsnag will keep track of the time and order of the breadcrumbs and show them on your dashboard.
Additional data can also be attached to breadcrumbs by providing the optional type and metadata parameters. For more information and examples for how custom breadcrumbs can be integrated, see Customizing breadcrumbs.
Session tracking
The BugSnag SDK tracks the number of “sessions” that happen within your application. This allows you to compare stability scores between releases on your dashboard and helps you to understand the quality of your releases.
Sessions are captured and reported by default. This behavior can be disabled using the autoTrackSessions configuration option.
BugSnag will automatically report a session each time the app is launched or enters the foreground after being in the background for at least 30 seconds.
For more information about controlling session tracking, see Capturing sessions.
Declaring feature flags and experiments
Monitor errors as you roll out features or run experiments and A/B tests by declaring your feature flag and experiment usage in the BugSnag SDK. You can use the Features dashboard to identify whether these features have introduced errors into your app.
[Bugsnag addFeatureFlagWithName:@"Checkout button color" variant:@"Blue"];
[Bugsnag addFeatureFlagWithName:@"New checkout flow"];
Bugsnag.addFeatureFlag(name: "Checkout button color", variant: "Blue")
Bugsnag.addFeatureFlag(name: "New checkout flow")
For more information, see Feature flags & experiments.
Identifying crashes at launch
By default BugSnag will identify crashes that occur whilst your app is launching, allowing you to prioritize fixing high-impact launch crashes.
Additionally you can use BugSnag to detect recurrent launch crashes: allowing you to take evasive action in your app, such as resetting data or turning off application features.
Follow the Identifying crashes at launch guide to configure this functionality.
Next steps
- View
bugsnag-cocoa, the library powering BugSnag for Apple Watch, on GitHub - Get support for your questions and feature requests