Native-first setup guide
If you have integrated Flutter screens into an existing Android or iOS app, follow this guide.
This documentation is for version 2 of the BugSnag Flutter library. We recommend upgrading to the latest release using our Upgrade guide. Documentation for the current release can be found here.
When your app is “native-first”, in other words you have added Flutter components to an Android or iOS app, you should start the iOS or Android BugSnag library as normal. In your Flutter module(s) you then “attach” to the running native BugSnag library. The Dart layer reads its configuration from the native layer.
If your app is “Flutter-first” (Flutter loads as as soon as your app starts), follow the main Flutter integration guide instead.
Installation
First follow the Android integration guide or iOS integration guide to add the BugSnag library to your app.
Then add bugsnag_flutter to your Flutter module with the flutter command line tool:
$ flutter pub add bugsnag_flutter
You can also manually add bugsnag_flutter to your pubspec.yaml:
dependencies:
bugsnag_flutter: ^2.0.0
The bugsnag_flutter package will add a dependency to the native BugSnag iOS and Android libraries using Cocoapods and Gradle respectively. For iOS, we recommend you remove the bugsnag-cocoa dependency that you added in the iOS integration guide so that a compatible version is installed via the bugsnag_flutter package. However for Android, you will need to keep the bugsnag-android dependency in Gradle if you wish to be able to build your app outside the flutter build command. Please ensure that the bugsnag-android dependency is kept up-to-date when you update your bugsnag_flutter package.
Basic configuration
The majority of the configuration is set in the native layer and picked up by bugsnag_flutter when you “attach”. Any configuration that only applies to bugsnag_flutter is set by importing the native bugsnag_flutter module in the native layer and modifying properties of the BugsnagFlutterConfiguration class.
To set up BugSnag in this way, add the following code to your Android or iOS app and Flutter module(s):
Android
Configure your API key in the <application> tag of your App Manifest file (usually in src/main/AndroidManifest.xml):
<application ...>
<meta-data android:name="com.bugsnag.android.API_KEY"
android:value="your-api-key-here"/>
</application>
You can find your API key in your project’s settings (shortcut: gs) in the dashboard.
Initialize BugSnag in the onCreate callback of your Application subclass (usually in MainApplication.java):
import com.bugsnag.android.Bugsnag;
import com.bugsnag.flutter.BugsnagFlutterConfiguration;
public class MainApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Bugsnag.start(this);
// Uncomment if you want to disable automatic detection of Dart errors:
// BugsnagFlutterConfiguration.enabledErrorTypes.dartErrors = false;
}
}
import com.bugsnag.android.Bugsnag
import com.bugsnag.flutter.BugsnagFlutterConfiguration
class MainApplication : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
Bugsnag.start(this)
// Uncomment if you want to disable automatic detection of Dart errors:
// BugsnagFlutterConfiguration.enabledErrorTypes.dartErrors = false
}
}
iOS
Configure your API key by adding a bugsnag Dictionary to your Info.plist file:
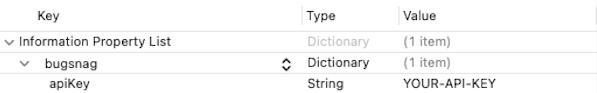
Or in XML:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>apiKey</key>
<string>YOUR-API-KEY</string>
</dict>
You can find your API key in your project’s settings (shortcut: gs) in the dashboard.
Import the Bugsnag module and initialize Bugsnag in your App Delegate’s application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: method.
Import the FlutterPluginRegistrant model and register Flutter’s GeneratedPluginRegistrant to initialize bugsnag_flutter’s plugin.
@import Bugsnag;
@import bugsnag_flutter;
@import Flutter;
@import FlutterPluginRegistrant;
@interface AppDelegate : FlutterAppDelegate
@property (nonatomic) FlutterEngine *flutterEngine;
@end
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
[Bugsnag start];
// Uncomment if you want to disable automatic detection of Dart errors:
// BugsnagFlutterConfiguration.enabledErrorTypes.dartErrors = NO;
self.flutterEngine = [[FlutterEngine alloc] initWithName:@"my flutter engine"];
[self.flutterEngine run];
// Connect plugins (bugsnag_flutter includes a plugin with iOS platform code).
[GeneratedPluginRegistrant registerWithRegistry:self.flutterEngine];
return [super application:application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:launchOptions];
}
@end
import Bugsnag
import bugsnag_flutter
import Flutter
import FlutterPluginRegistrant
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: FlutterAppDelegate {
var flutterEngine = FlutterEngine(name: "my flutter engine")
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions
launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
Bugsnag.start()
// Uncomment if you want to disable automatic detection of Dart errors:
// BugsnagFlutterConfiguration.enabledErrorTypes.dartErrors = false
flutterEngine.run();
// Connect plugins (bugsnag_flutter includes a plugin with iOS platform code).
GeneratedPluginRegistrant.register(with: flutterEngine)
return super.application(application, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: launchOptions);
}
}
If your app adopts the SwiftUI App Life Cycle, adapt the code found in our iOS integration guide accordingly.
Flutter
In your Flutter module, attach to the running native BugSnag library by using bugsnag.attach to wrap your main function’s call to runApp (usually in main.dart):
import 'package:bugsnag_flutter/bugsnag_flutter.dart';
void main() async => bugsnag.attach(runApp: () => runApp(const MyApp()));
Next steps
Head back to the Flutter integration guide and pick up where you left off.