Manual setup guide
The easiest way to get started with BugSnag on a React Native project is to use our CLI, as detailed in the installation and configuration guide. If your project structure deviates from a normal setup, or you just want to make the modifications to your project manually, you can follow this guide.
These docs are for the @bugsnag/react-native package, which supports React Native v0.60 and above.
If you’re using the previous bugsnag-react-native package, we recommend upgrading to the latest release, unless you’re using a version of React Native older than 0.60. Documentation for bugsnag-react-native can be found on our legacy pages.
Installation
Add the BugSnag package to your dependencies in package.json:
npm install --save @bugsnag/react-native
# or
yarn add @bugsnag/react-native
The latest available version of @bugsnag/react-native is v8.7.0.
To ensure errors that occur before React Native initializes are captured, BugSnag is started and configured in the native Android and iOS projects. These dependencies are added automatically to your Gradle and CocoaPods configuration.
To complete the installation, open the ios/ subdirectory of the project and run pod install:
cd ios/ && pod install
Basic configuration
The BugSnag React Native package uses the native BugSnag Cocoa and Android libraries to send both native and JavaScript errors to your dashboard. To setup your app, add the following code to your Android project, Xcode project and your JavaScript code:
Android
Configure your API key in the <application> tag of your App Manifest file (usually in src/main/AndroidManifest.xml):
<application ...>
<meta-data android:name="com.bugsnag.android.API_KEY"
android:value="your-api-key-here"/>
</application>
You can find your API key in your project’s settings (shortcut: gs) in the dashboard.
Initialize BugSnag in the onCreate callback of your Application subclass (usually in MainApplication.java):
import com.bugsnag.android.Bugsnag;
public class MainApplication extends Application implements ReactApplication {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Bugsnag.start(this);
// ...
}
}
import com.bugsnag.android.Bugsnag
class MainApplication : Application(), ReactApplication {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
Bugsnag.start(this)
// ...
}
}
iOS
Configure your API key by adding a bugsnag Dictionary to your Info.plist file:
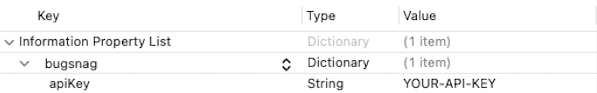
Or in XML:
<key>bugsnag</key>
<dict>
<key>apiKey</key>
<string>YOUR-API-KEY</string>
</dict>
You can find your API key in your project’s settings (shortcut: gs) in the dashboard.
App Delegate
If your app implements an app delegate, import the Bugsnag module and initialize Bugsnag in the application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: method:
#import <Bugsnag/Bugsnag.h>
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
[Bugsnag start];
return YES;
}
import Bugsnag
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
func application(_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions:
[UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
Bugsnag.start()
return true
}
}
JavaScript
In index.js, import and start the BugSnag JavaScript client:
import Bugsnag from '@bugsnag/react-native'
Bugsnag.start()
If you’re using App Center CodePush you should set the codeBundleId configuration option.
Next steps
- Head back to the Integration guide and pick up where you left off.
- See the Showing full stacktraces guide to find out how to see the original method names, file paths, and line numbers in stacktraces.